RONGKE
Induction furnaces for melting, holding and casting
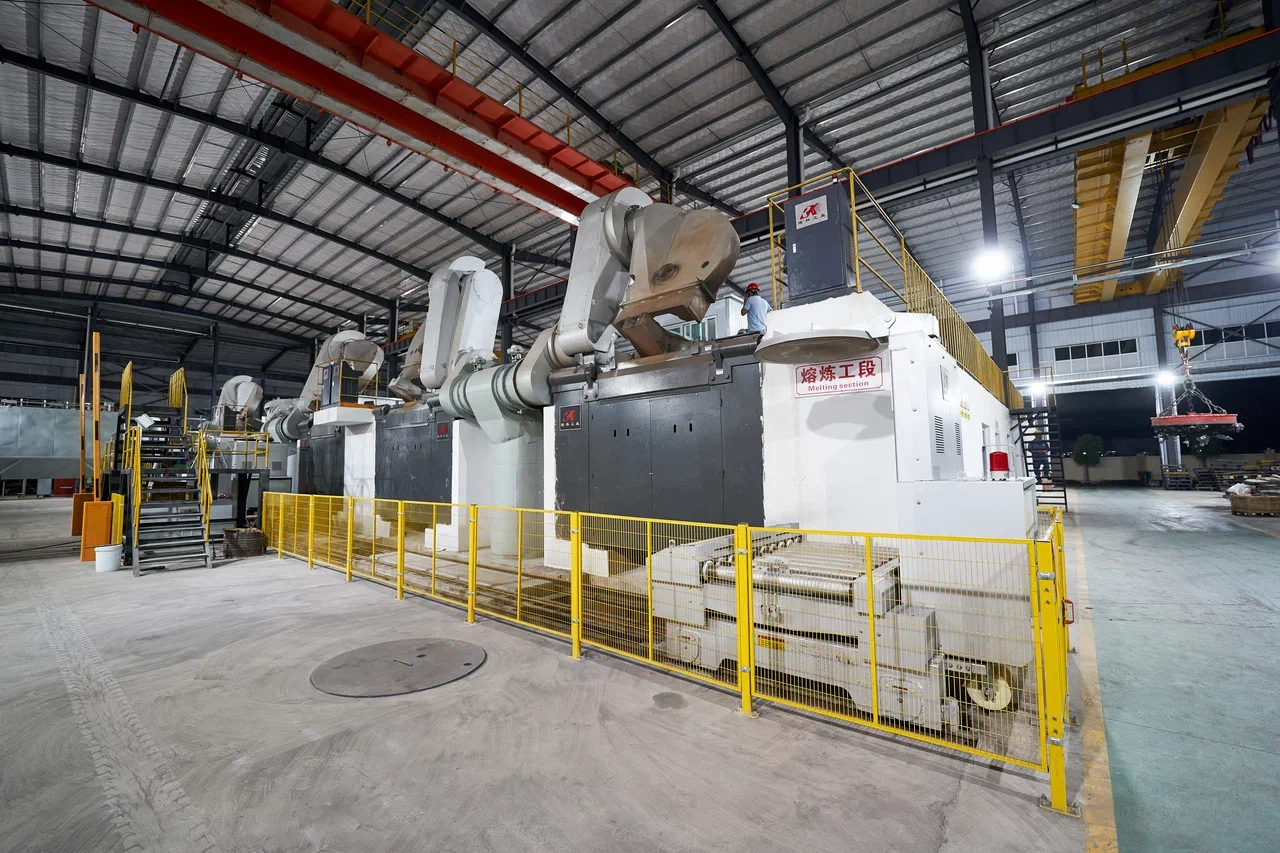
GUANGDONG RONGKE INDUSTRIAL EQUIPMENT (PRC) manufactures medium frequency induction furnaces for melting, holding and casting ferrous and non-ferrous metals. Located in Shunde District, Foshan, Guangdong Province, is a high-tech enterprise integrating research, development, production and operation.
At present, the company employs more than 200 people, 30 of whom are involved in R&D, development and implementation of new technologies. The products include intermediate frequency induction melting and heating systems, automatic dosing and feeding systems, electric furnace cooling systems, automatic pouring systems, automatic molten iron transport systems and dust removal systems.
Our company is one of the few suppliers of complete melting systems, and our products are widely used all over the world. They are used in such comprehensive enterprises as ferrous and non-ferrous metal polymetallic casting, steel industry, electrolytic aluminium industry, vacuum melting, heat treatment, powder metallurgy, precious metal smelting and refining.
As of 2024, the company has manufactured more than 1,600 units of melting plants with a capacity of up to 18 MW on thyristor converters and up to 10 MW on transistor converters (IGBT).
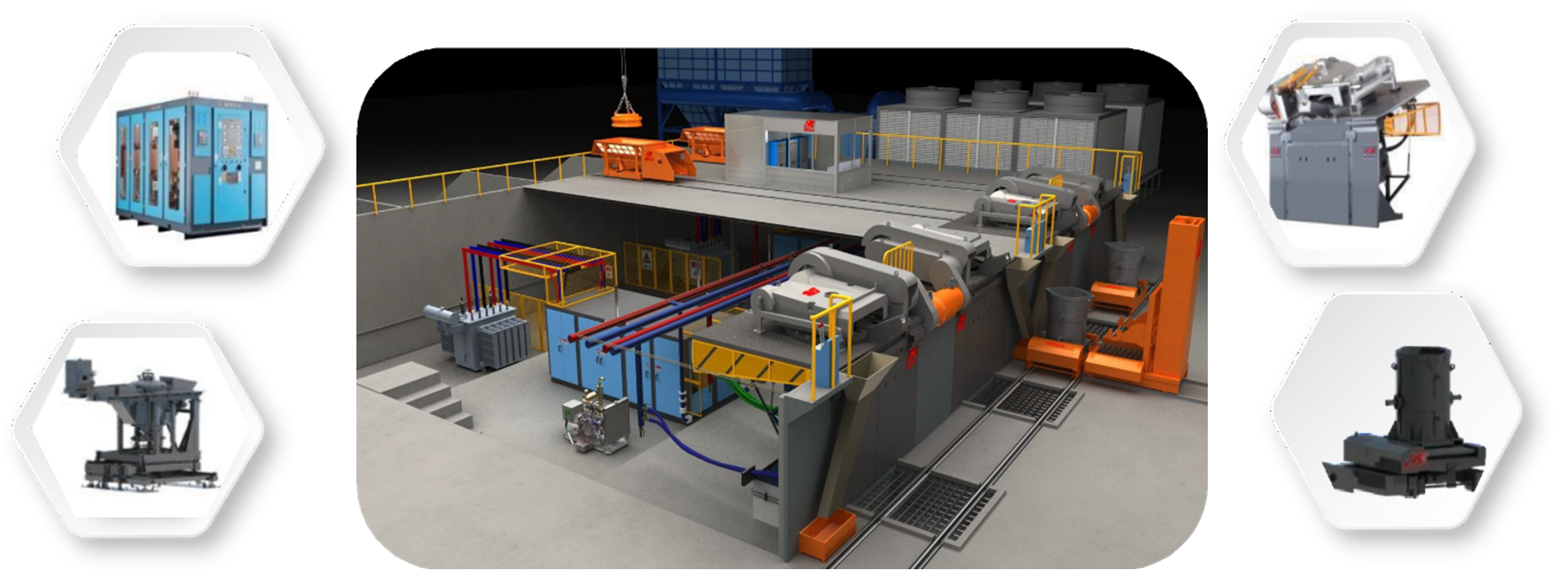
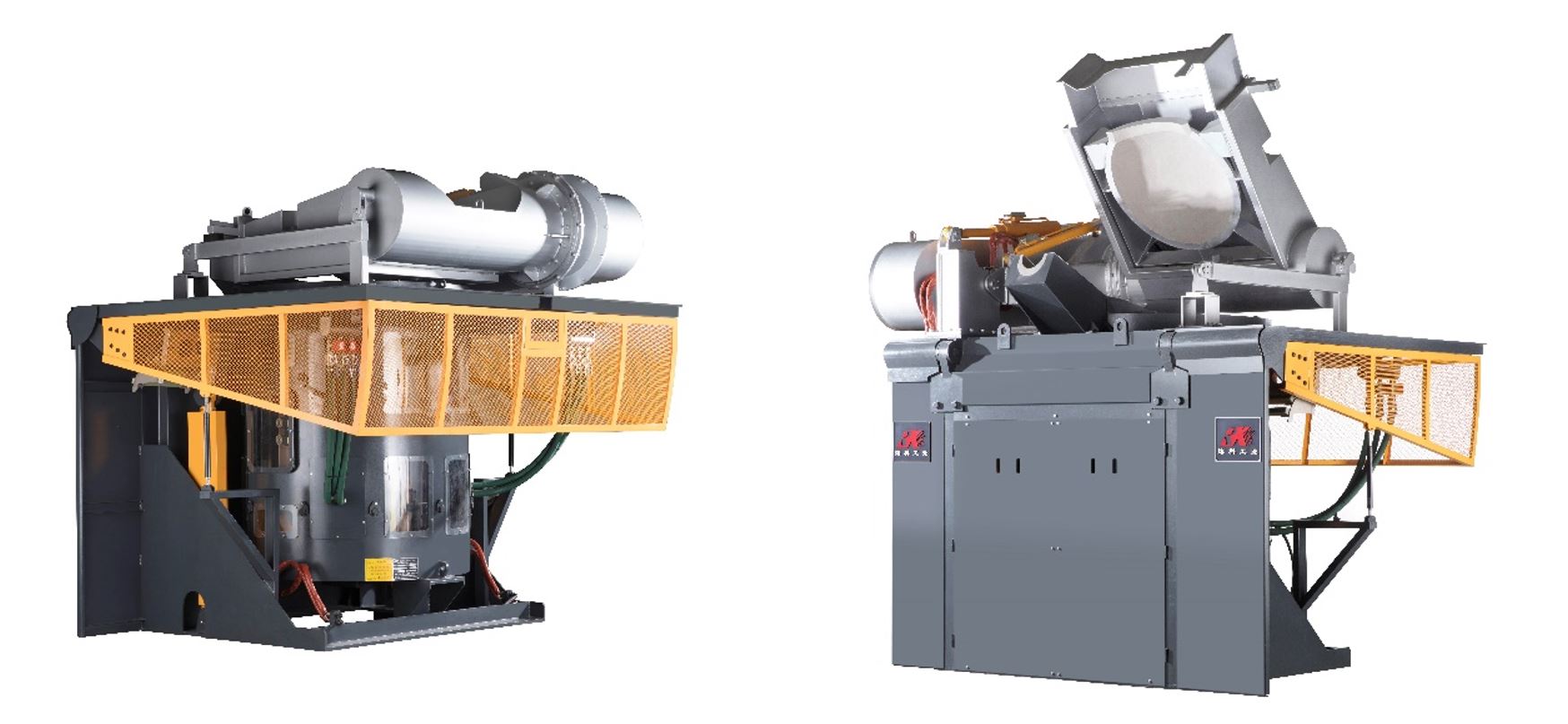
Medium-frequency induction melting crucible furnaces
The technical and economic advantages of RONGKE medium-frequency induction crucible furnaces are the reason for their increasing use in the foundry industry.

Economic Characteristics:
- Low energy consumption;
- Low melting losses;
- High plant availability;
- Easy operation and maintenance;
- Low installation costs due to compact design;
- Minimal installation time due to pre-assembled units;
- Low labour costs due to automated melting process.
Specifications:
- Strict temperature and process control;
- High precision and reproducibility of analyses;
- High productivity due to high power efficiency;
- High operational flexibility / easy switching between different types and grades of metals;
- Possibility of melting with and without bogging.
New efficient RONGKE developments to reduce melting costs:
- A system for smooth distribution of converter power between two furnaces;
- The «multi-frequency» melting frequency switching technology. With this technology, melting starts at the optimum frequency (250 Hz) and then switches to a lower frequency (125 Hz) to increase bath agitation for melt alloying/supercharging;
- The melting processor provides optimum process control;
- The optical inductor protection system is a new generation of temperature monitoring in the furnace working zone using fiber optic sensors.
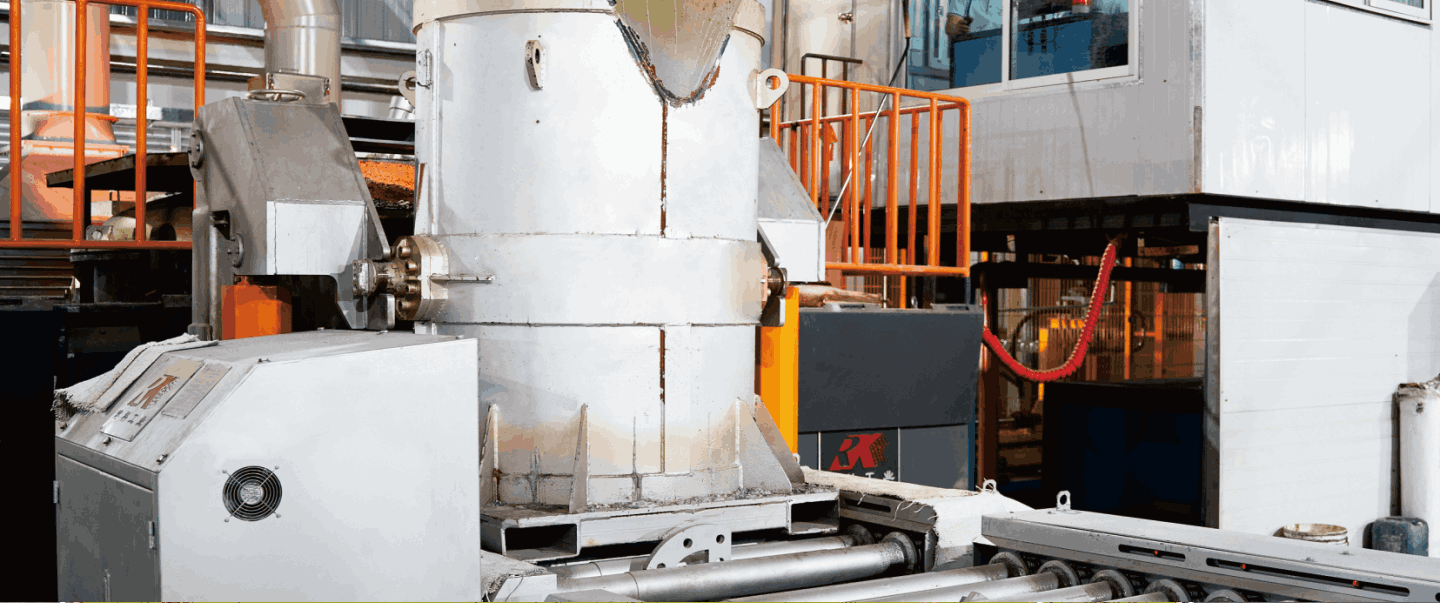
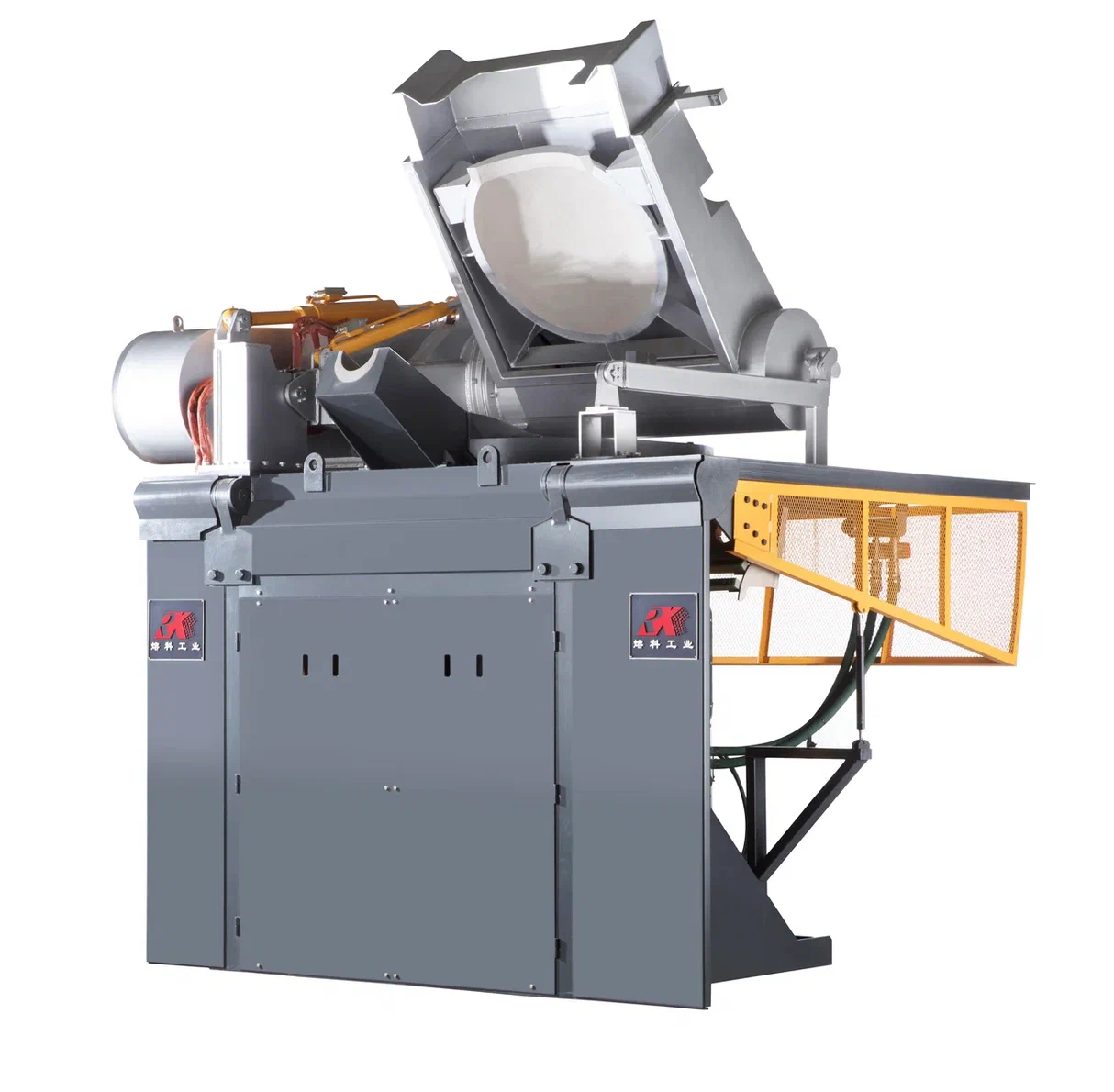
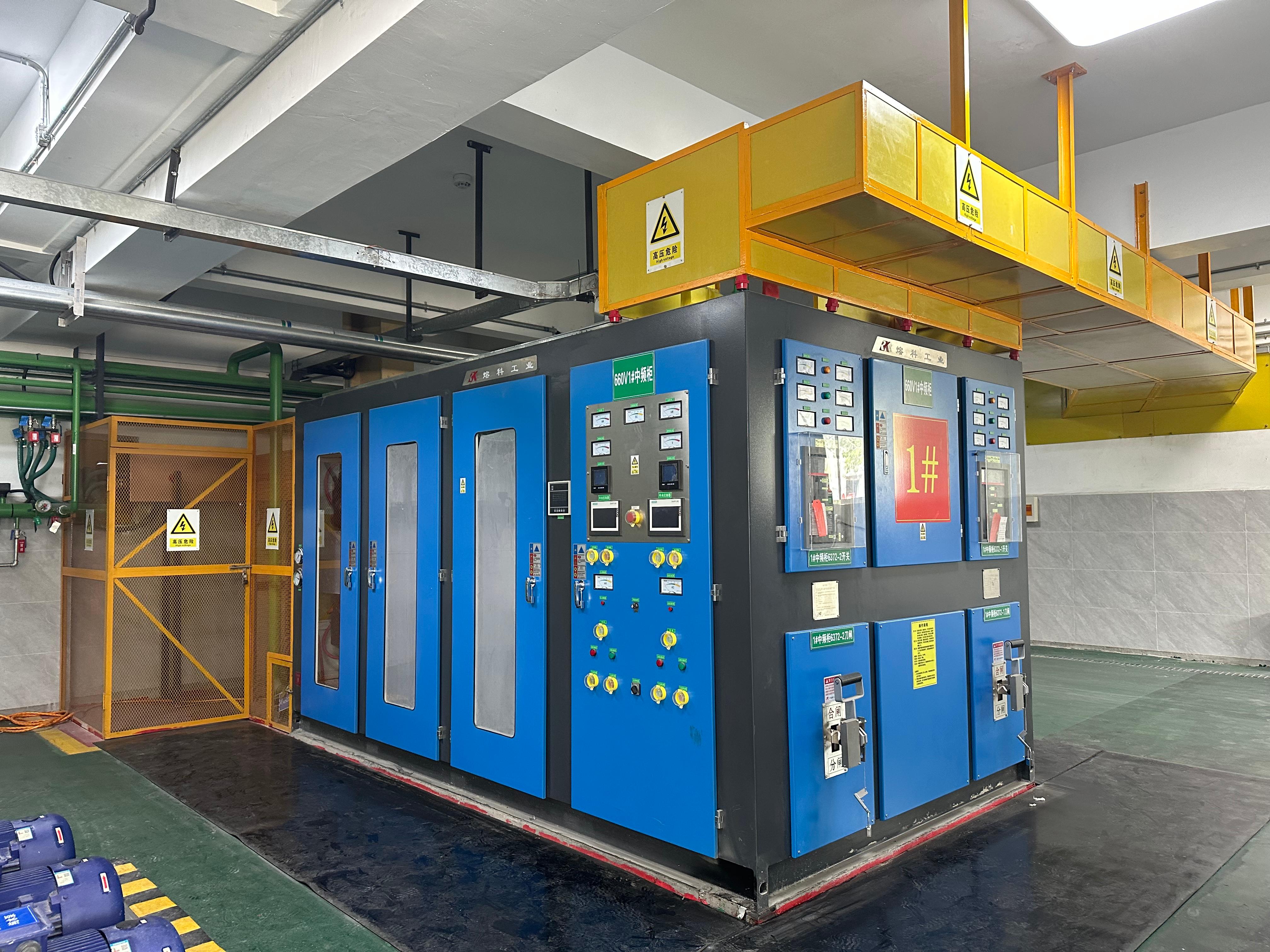
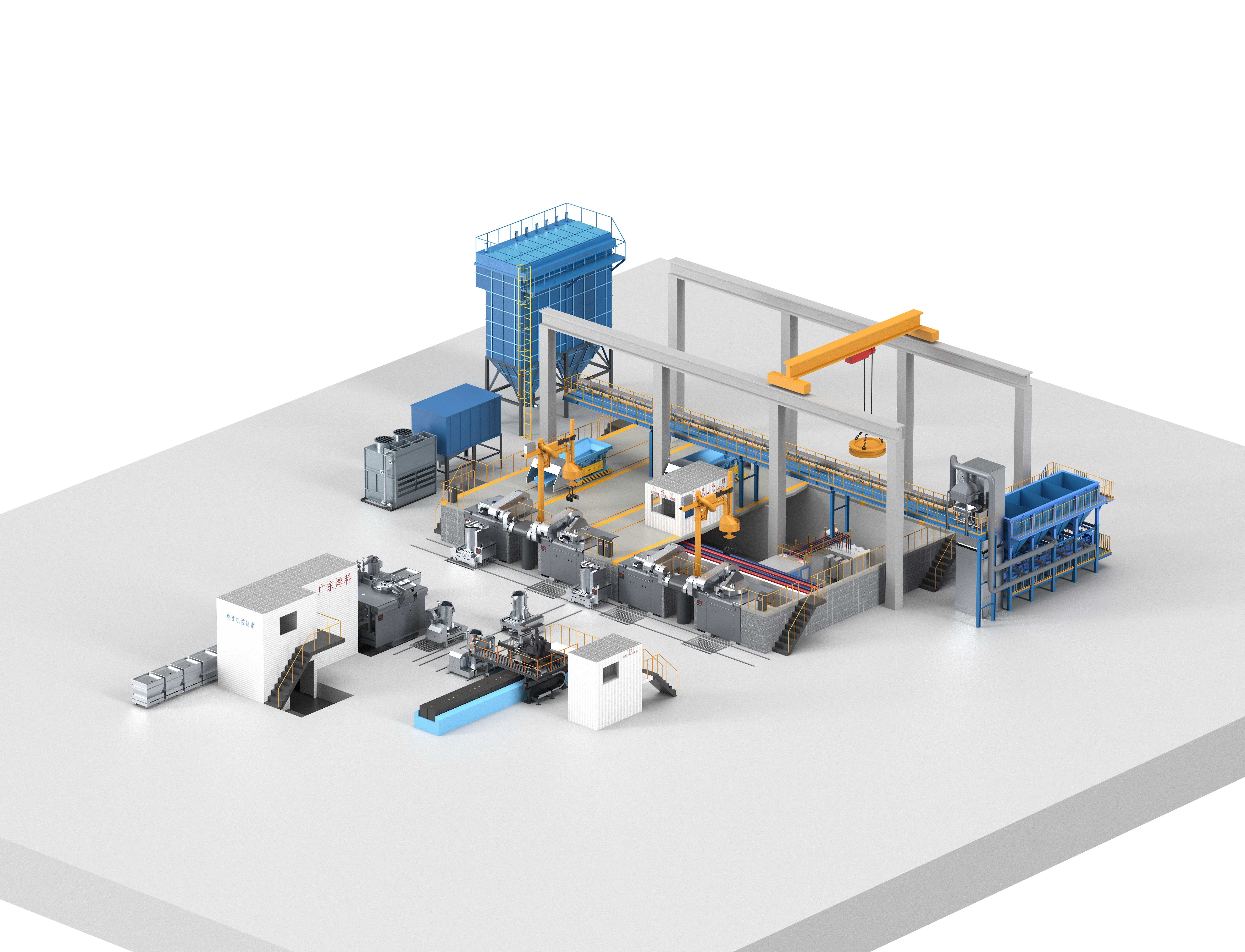
A medium frequency crucible furnace plant comprises:
A melting furnace including:
- Furnace body with inductor;
- Inclined furnace frame (optionally with reverse inclination);
- Hydraulic station;
- Furnace pit guard;
- Operator panel;
- Exhaust hood, hydraulically openable in two directions.
The powerhouse, including:
- Rectifier transformer;
- Frequency converter;
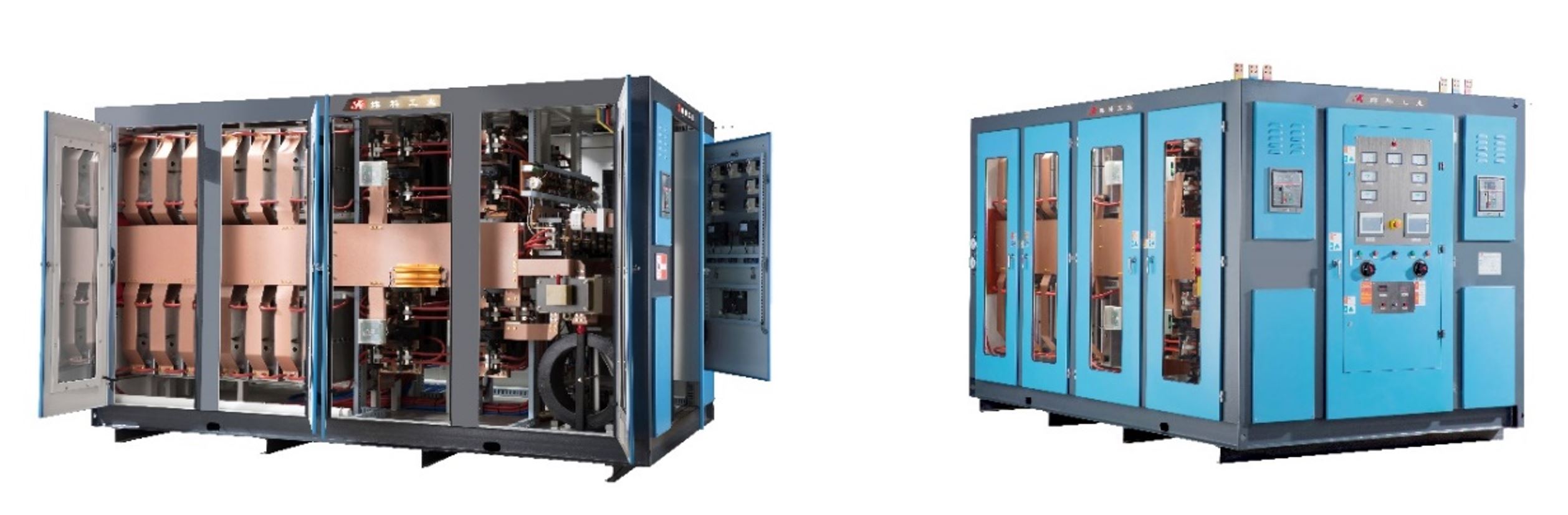

- Capacitor module;
- Power cables.
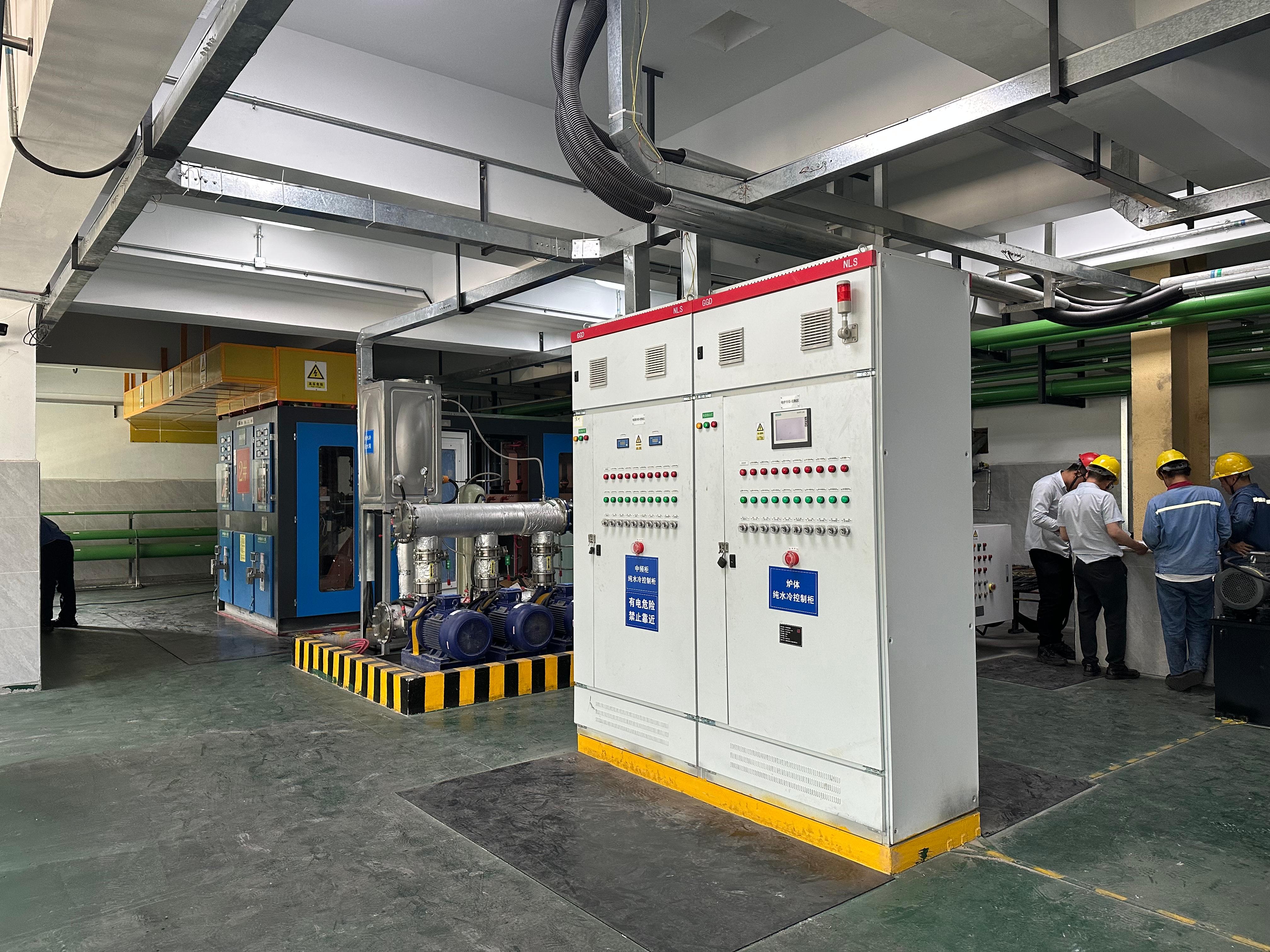
Process control systems including:
- Weighing system;
- Control cabinet;
- Melting processor;
- Optical coil protection system.

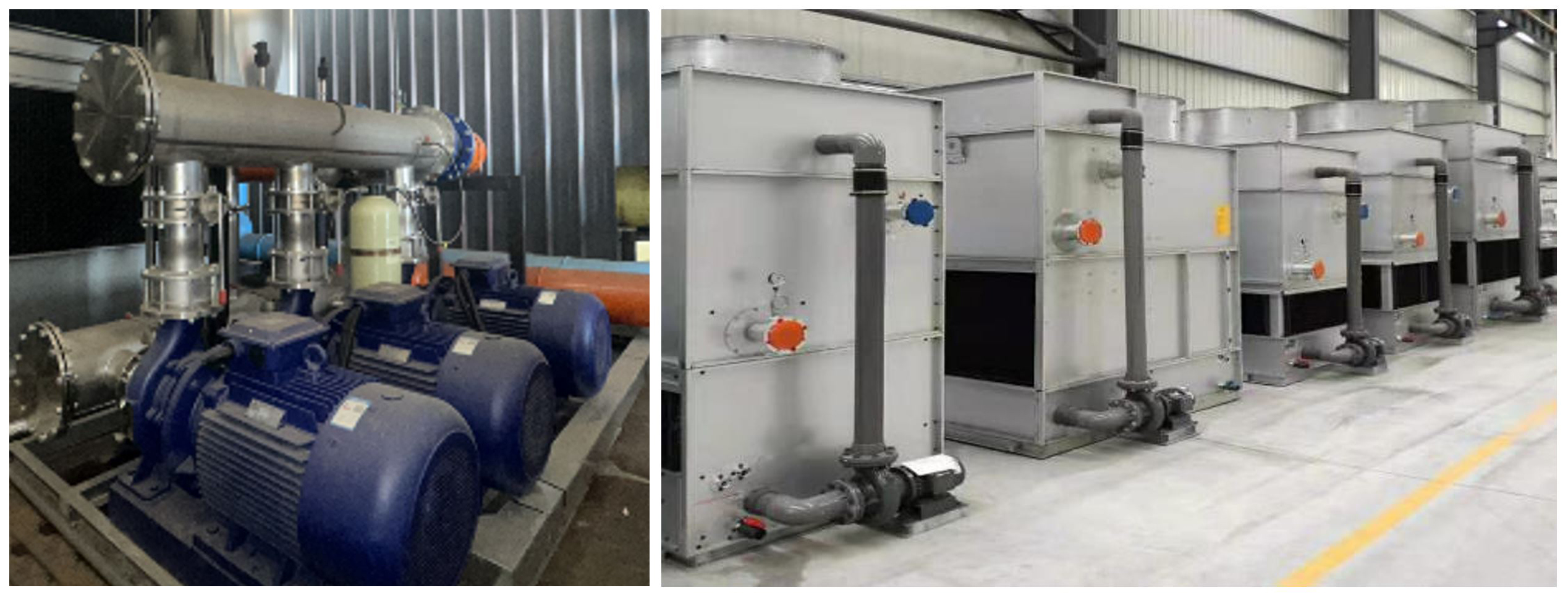
Furnace and Power Unit Water Cooling Systems with Air Cooler / Cooling Tower

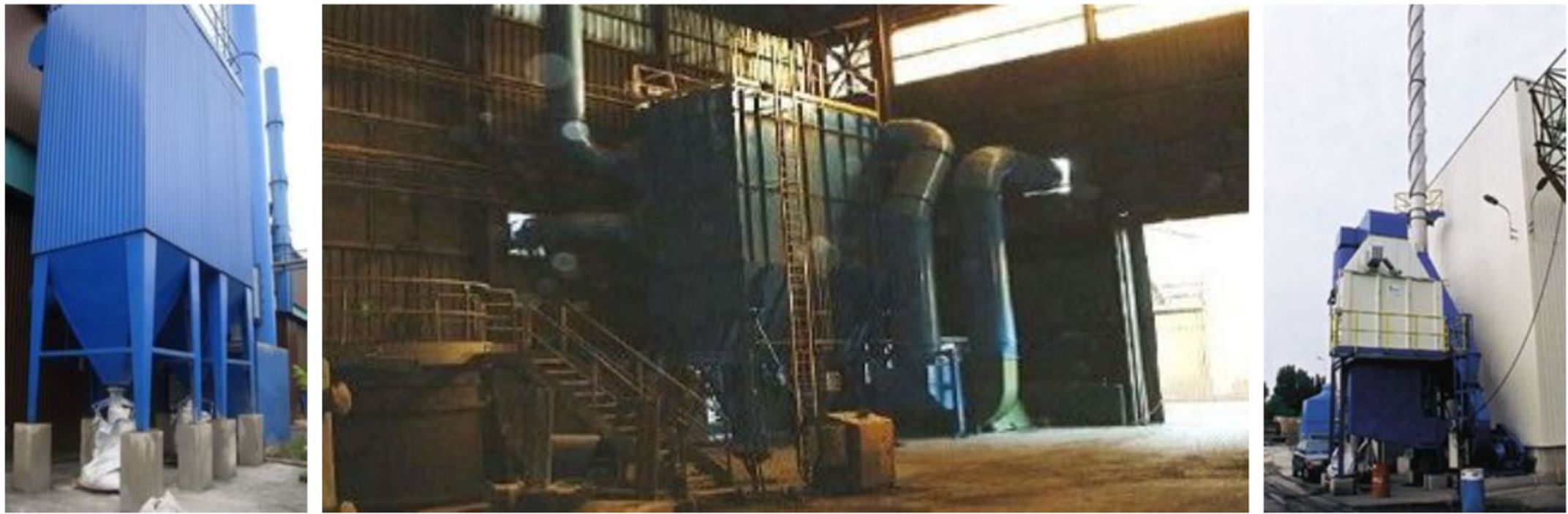
Auxiliary equipment including:
- Dust collection system;

- Charging equipment;
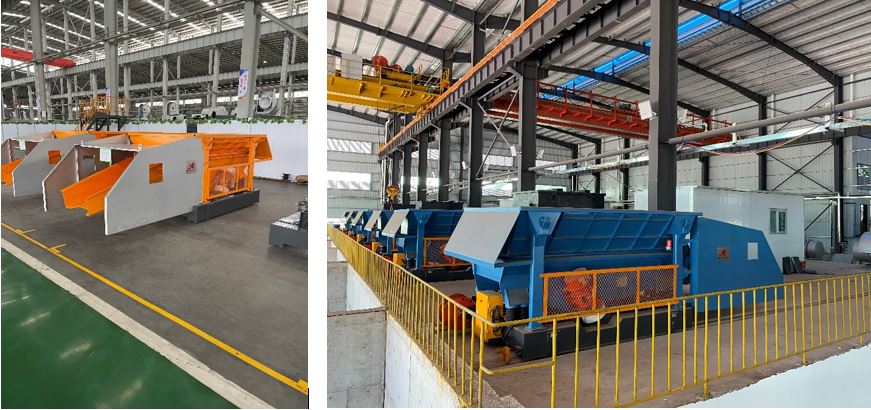

- Crucible ejection system.
Efficient developments to reduce smelting costs
1. Power distribution system between the furnaces
Smooth distribution of frequency converter power between two furnaces operating in series
- Full and constant utilization of 100% of rated power;
- Shorter downtimes for higher productivity;
- Simultaneous melting, holding and casting;
- Maximum flexibility.
2. System for switching power between furnaces
- Switching 100% power supply between two furnaces operating in series;
- Shorter downtimes for higher productivity;
- Simultaneous melting, seasoning and casting.
3. Multi-frequency technology
This technology is based on changing the melting frequency to optimize the melting results. Such a process may involve steps starting with an increased frequency adapted to the coarseness of the charge material grains (250 Hz), followed by a decrease in frequency automatically after the metal has melted, in order to increase the turbulence of the furnace bath to enhance the mixing effect and the assimilation of alloying elements. If a smooth bath surface is required in the superheating phase, the frequency must be increased (125 Hz).
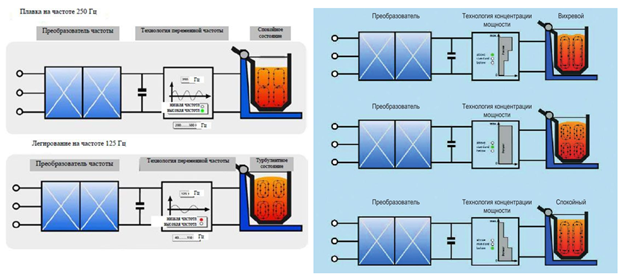
Features of application of multi-frequency technology:
- Rapid melting of fine lump material;
- Optimum correction of chemical composition (carbon content adjustment);
- Minimal metal oxidation;
- Minimal melting losses;
- Reduced energy consumption per tonne of liquid material;
- Optimum utilization of power consumption.
4. Melting processor
The melting processor ensures optimum process control and reliable monitoring of the entire melting process. It provides automatic control of all functions and processes related to melting, exchanges data and information with higher-level control systems, and analyses and records operating data.
The scope of functions includes:
- Automation;
- Monitoring;
- Process documentation.
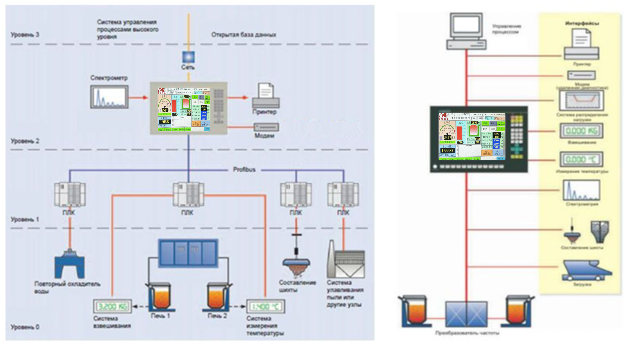
The system can perform the entire process chain from charge formulation, loading and melting to analysing, correcting and controlling all auxiliary units and peripheral equipment.
Principle of operation:
All actual data collected by sensors and PLC systems are compared with specified parameters and setpoints to calculate and control:
- the amount of energy for melting, holding and superheating;
- sintering time;
- temperature and cold start modes;
- charge composition;
- analyzing and correcting the melting process;
- furnace data and safety functions.
The main menu contains various submenus which the operator can select using the assigned function keys. At the same time, a brief description of the status of the equipment is displayed at the top of the window for continuous monitoring.
5. Optical coil protection system

Represents the new generation of temperature measurement and monitoring in the furnace working area using fibre optic sensors. Due to their measuring characteristics, such sensors are particularly good at providing interference-free measurement on crucibles in induction melting furnaces.
The optical system is thus a unique monitoring system that for the first time makes it possible to determine the temperature field in an induction furnace regardless of the type and construction of the refractory.
Physical principle of operation
Based on the optical fiber, the system applies a quantum mechanical effect, the so-called «combination scattering» (Raman effect), to measure the temperature. The system feeds laser radiation with a suitable wavelength and modulation frequency into the optical fiber. This laser radiation is scattered on the binding electrons of the structure along the entire length of the fiber and is detected as a backscatter spectrum.
This spectrum contains Raman lines whose intensity is functionally dependent on the vibration of the solid-state fiber structure, which in turn depends on temperature. The new patented «optical radar method» makes it possible to locally detect such lines as well as to measure an accurate, high-resolution temperature profile around the circumference of the crucible in real time.
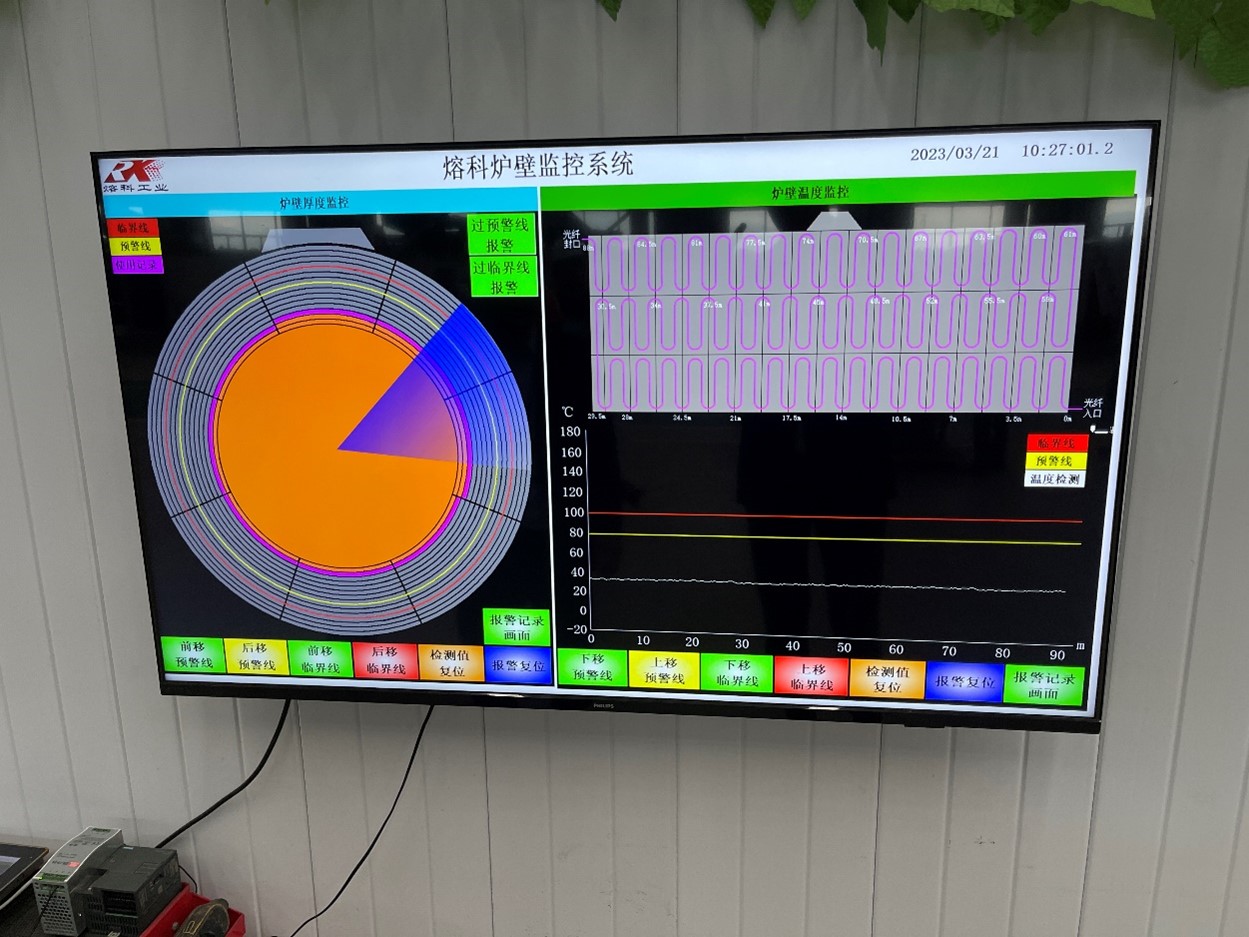
Functions of the coil protection system
- Visualization of the temperature as well as the temperature difference over a period of time in the immediate vicinity of the inductor;
- Evaluation of crucible life;
- Temperature differential signalling;
- Signalling when the set maximum temperature is exceeded.
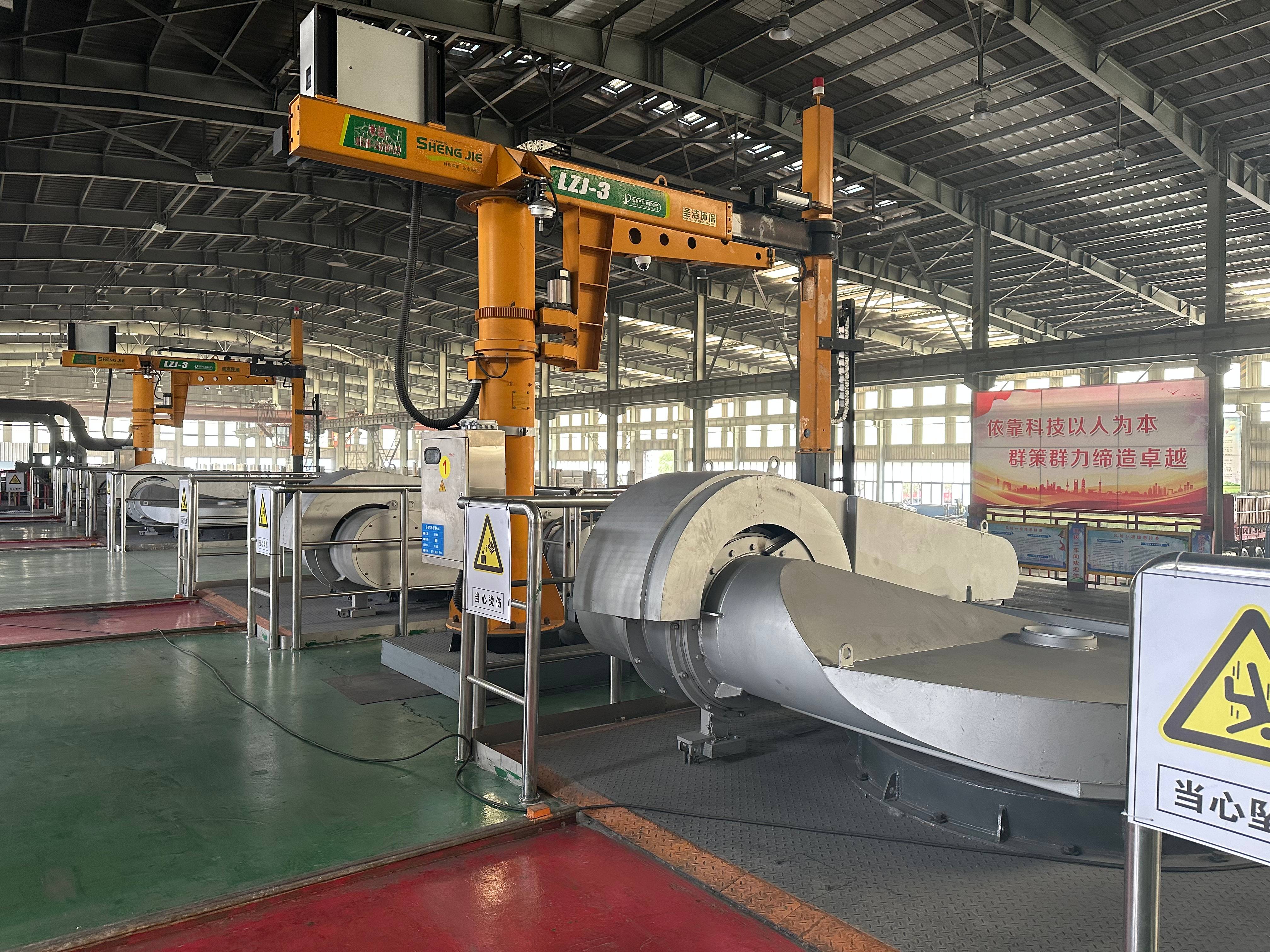
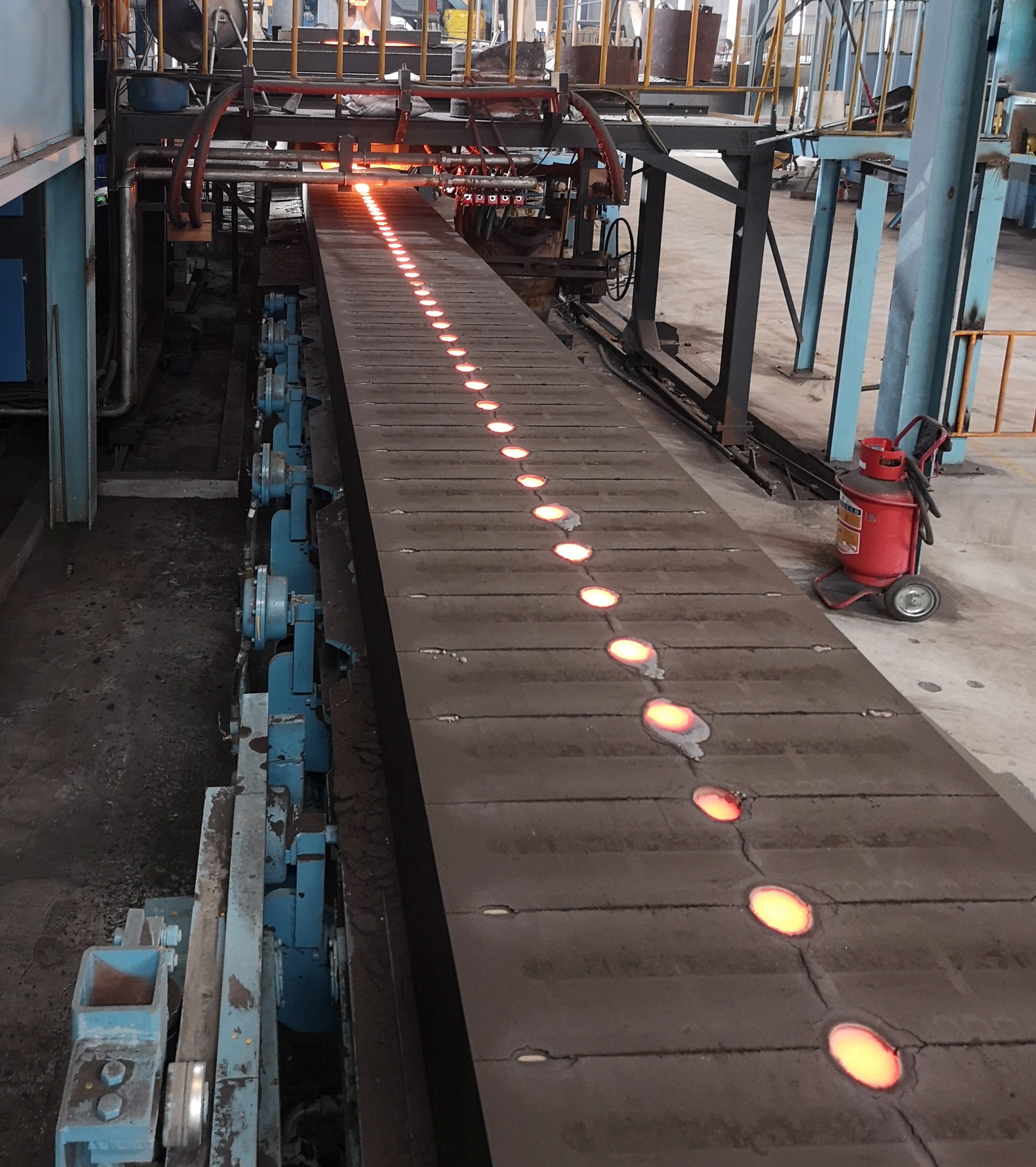
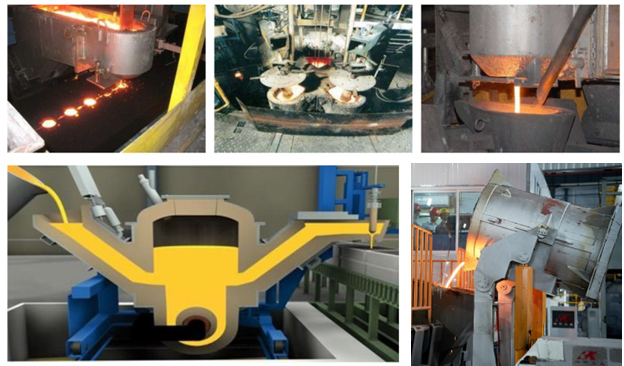
Induction-heated casting furnaces
The casting furnace consists of a cylindrical furnace tank with filling port and siphon type discharge chute, and includes a stop mechanism. Easily replaceable inductor with flange mount at the bottom. The pouring port and discharge chute can be positioned at an angle of +/- 90° or 180° to each other. The pouring furnace is mounted on a double trolley to be able to move along and across the mold line and thus to approach pouring the sprue funnels, which can be located in different parts of the mold.
Application area:
- Flask molding lines;
- Flaskless molding lines;
- Plants for the production of high quality copper anodes;
- Centrifugal casting machines;
- Intermediate ladle casting.
Regulation of metal level in the outlet chute of casting furnaces is carried out by means of:
1. Float system
A ceramic float is immersed in the liquid metal. When the level of the bath changes, a change in buoyancy is detected and the casting pressure is adjusted so that the metal level comes back to the set level.

2. System with laser
Non-contact bath level detection is carried out by means of a laser system. The set metal level remains constant by adapting the casting pressure.

3. Protective electrodes
These electrodes limit the maximum allowable metal level in the discharge chute. When the electrodes come in contact with the liquid metal, a momentary safety release occurs, causing the liquid metal to flow back from the discharge chute into the furnace tank.

Economic aspects of using RONGKE casting furnaces
- reduced production scrap during casting;
- no residual pig iron and increased ladle economy;
- increased productivity due to optimum utilisation of the molding machine;
- the casting process is independent of the melting shop;
- labour cost savings;
- improved working conditions.